To understand what is the trade we must have some historical and economic facts in our minds.
By Guy Avtalyon
What is trade? For some of you, this question may seem like nonsense. But, do we all know what is a trade for sure? So, let me explain this. Trade is a basic economic concept that involves the buying and selling of goods and services. Trading points to the buying and selling of securities, for example, buying and selling stock.
Answer to this question could be: Trade is a transfer of goods or services in return for money, services or goods. In other words, trade refers to give and take. In the old days, trade took place with the exchange of goods without the exchange of money. With the invention of money, the trade appeared as an exchange of things for money.
Trade is buying and selling on stock market transactions with the help of stock market brokerage houses. To trade in capital markets, one has to learn technical analysis first. Then apply those learned technical analysis concepts through paper-trading for a few weeks then open a trading account thru a broker and slow start the first real trade.
Everybody knows what the term “trade” means. We are trading in our everyday life, while we may not even register that we have done so. Basically, everything we buy in a market is trading money for the goods we need.
So, what is the trade?
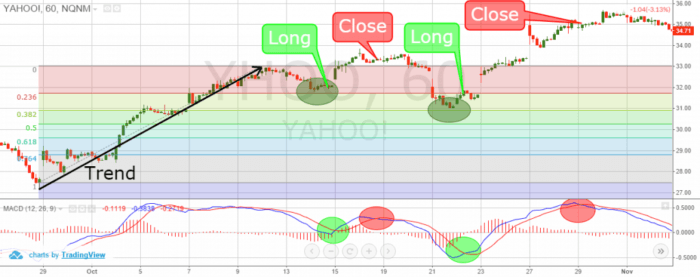
The word “trade” simply means “exchange one thing for another”. We normally get this to be the changing of goods for money or in other words, simply buying something. The same principle is applied when we trade in the financial markets. Let’s say someone trades shares. What traders and investors are really doing is buying shares of some companies. When the value of the shares rises, they will make money if sell them at a higher price. This is trade. You buy something for one price and sell it again for another, hence making a profit or loss.
Why traders trade
Every single trader is buying the shares in the hope that the price will rise. But why would the value of the shares go up? The answer is simple: the value changes due to supply and demand, meaning the more demand there is for something, the more people are willing to pay for it.
Trade is conducted not only for the sake of earning a profit; it also provides service to the consumers. Trade is an important social activity because society needs an uninterrupted supply of goods forever increasing and ever-changing but never-ending human wants. Trade exists from the beginning of human life and will obviously last as long as human life exists on the globe. It enhances the standard of living of consumers. Thus we can say, answering the question of what is the trade, that trade is a very important social activity.
The examples of what is a trade
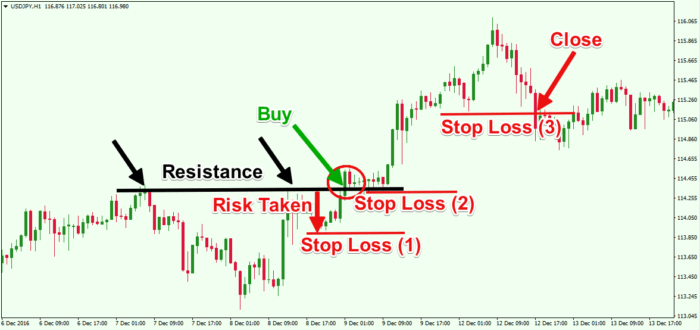
Trade is when two parties agree on the price of a financial instrument but they perceive it’s valued differently.
For example, say, trader A wants to buy stock with the current market price of $800. So, when trader A buys a stock at $800 there is a seller trader B at the same price. Hence, both of them have an agreement at the price of $800. But the buyer, trader A values is higher than the seller, trader B at that point.
Let’s say that suddenly the owner of another stock comes into the market and has even more stocks to sell. The supply of stocks has now increased dramatically. Now, it’s reasonable to expect the second trader will want to sell that stock at a lower price than the first one to attract the other traders to buy that stock. And such will be right. The other traders would reasonably want to buy at the lower price, why not. Let’s see what happened with the first trader. The first trader will lower the stock price also.
Can you see how the sudden increase in supply has brought the price of the stocks down?
When the asset’s price at which demand matches supply is known as the “market price”. In other words, that is the price at which traders agree on both sides, sellers and buyers both.
Trade is executed with the payment of money, the transaction of goods and services, or virtual currency.
What is the trade of virtual currencies
Those who want to trade cryptocurrency should start by picking a company with a good status that gives an exchange and wallet. The beginners should start by trading leading coins. Currently, we are referring to coins like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). In the future, this could change.
Cryptocurrencies are still new to some people, so trading in this novelty can certainly generate good outcomes. But it is important that you know very well what any virtual currency gives and know the features of each coin. It is necessary for you to make trading informed decisions, evaluating carefully the risks/benefits of each coin. Using a reputable cryptocurrency exchange platform could support you in order to take the best possible of cryptocurrency trading.
Virtual currencies
Virtual currencies do not expose holders to foreign exchange risks and provide anonymity between trading partners. Some online resellers provide buyers to conduct their transactions using virtual currencies. If you want to trade cryptos you can also find platforms that convert virtual currencies into gift cards. Virtual currencies are often popular with small businesses, because of the lack of processing fees.
Trading cryptocurrency isn’t hard to start, but there are some basic aspects to understand before you start trading with a wallet-exchange.
The main thing to note is that there are countless options for setting up wallets and trading currency.
The bottom line
When we ask what is the trade we should have some historical and economic facts in our minds. The process of economic specialization and trade leads to much higher levels of production of goods and services. It is this process that creates and sustains the markets of the “free market” system. The development of this system brought about the dramatic and revolutionary improvements in living standards that characterize the modern age.
Free and open trade has fired competition, innovation, and economies. It allows individuals and businesses to take advantage of lower prices and increased choice. As a consequence, millions of people all over the world have overcome the restrictions of subsistence farming and severe poverty that defined the lives of most of humankind during history.